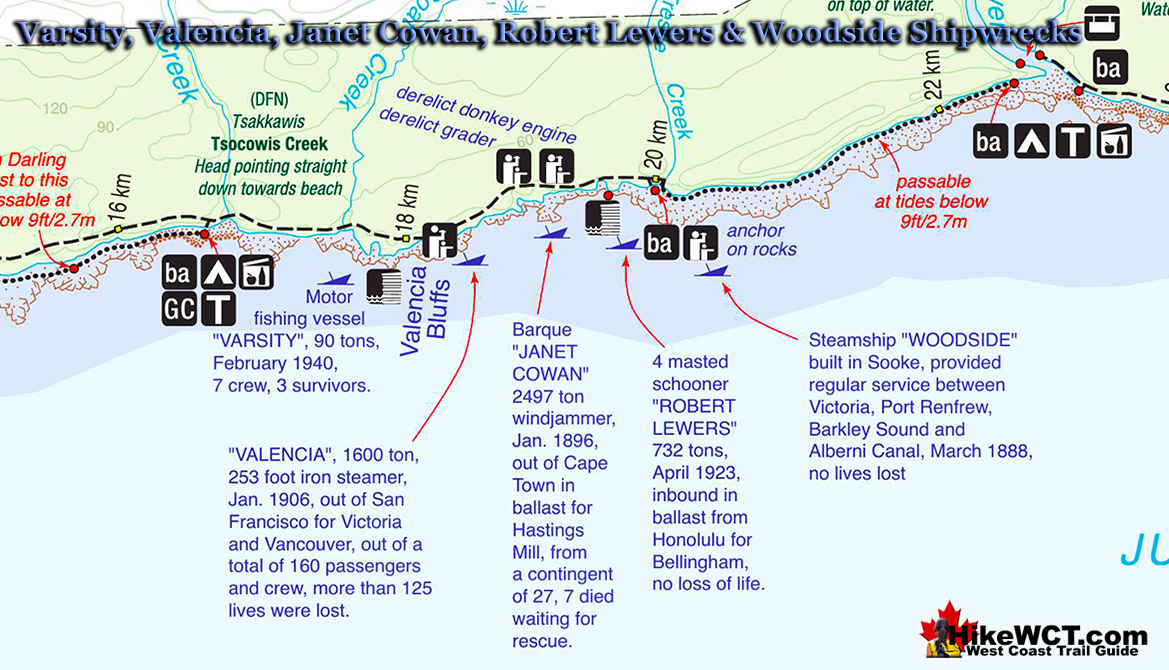
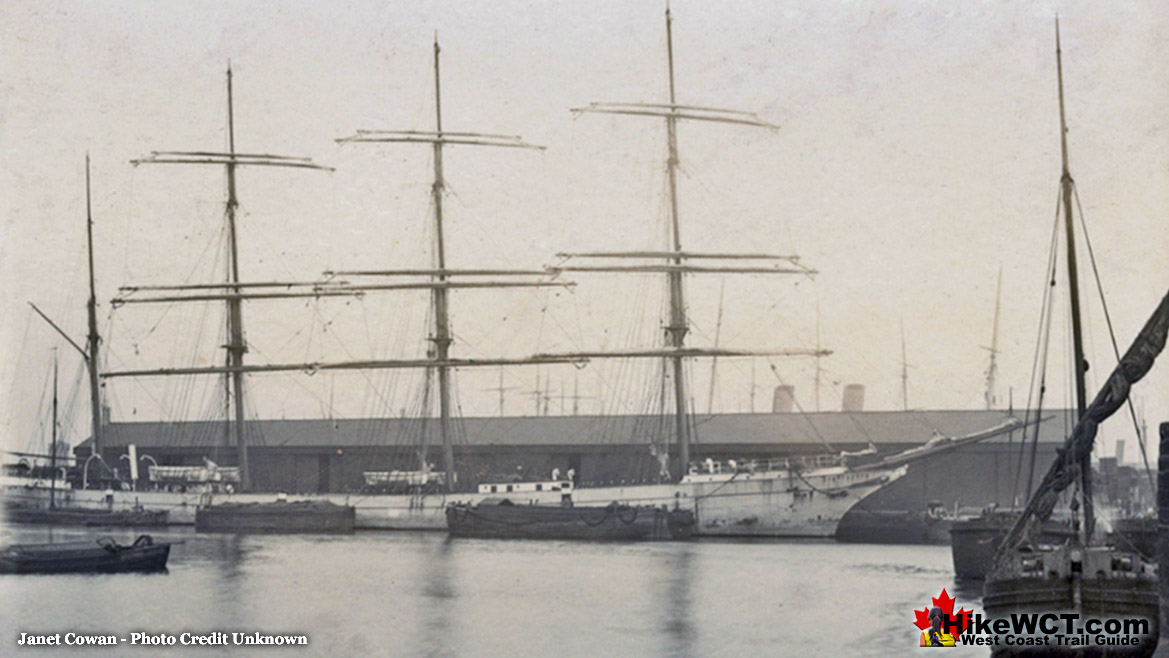
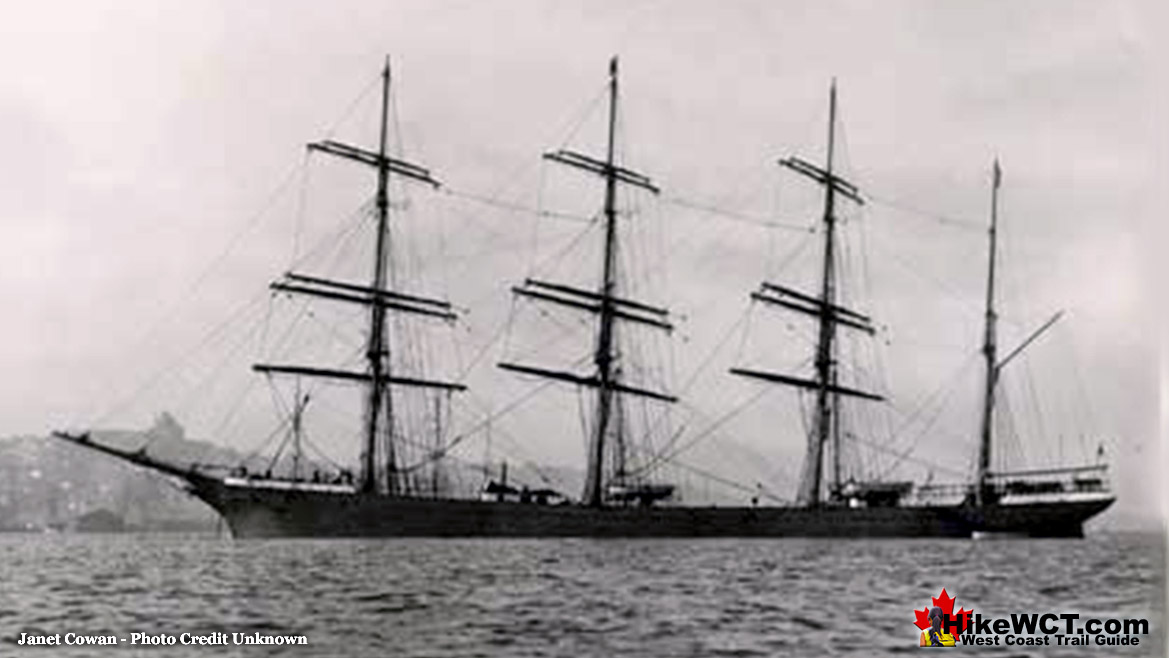
![]() The Janet Cowan was a steel sailing vessel, four-masted, bark rigged, of 2498 tons built at Glasgow in 1889. She was wrecked at about the 19 kilometre mark on the West Coast Trail with several lives lost. The Janet Cowan shipwreck shone a light on the necessity of building more lighthouses and constructing a coastal lifesaving trail. Little was done, however, and just 10 years later, and less than a kilometre away, the Valencia met a similar fate.
The Janet Cowan was a steel sailing vessel, four-masted, bark rigged, of 2498 tons built at Glasgow in 1889. She was wrecked at about the 19 kilometre mark on the West Coast Trail with several lives lost. The Janet Cowan shipwreck shone a light on the necessity of building more lighthouses and constructing a coastal lifesaving trail. Little was done, however, and just 10 years later, and less than a kilometre away, the Valencia met a similar fate.
 Alaskan Shipwreck at 4km
Alaskan Shipwreck at 4km Soquel Shipwreck at 5km
Soquel Shipwreck at 5km Sarah Shipwreck at 7km
Sarah Shipwreck at 7km Becherdass-Ambiadass Shipwreck at 8km
Becherdass-Ambiadass Shipwreck at 8km Michigan Shipwreck at 12km
Michigan Shipwreck at 12km Uzbekistan Shipwreck at 13.8km
Uzbekistan Shipwreck at 13.8km Varsity Shipwreck at 17.6km
Varsity Shipwreck at 17.6km Valencia Shipwreck at 18.3km
Valencia Shipwreck at 18.3km Janet Cowan Shipwreck at 19km
Janet Cowan Shipwreck at 19km Robert Lewers Shipwreck at 20km
Robert Lewers Shipwreck at 20km Woodside Shipwreck at 20.2km
Woodside Shipwreck at 20.2km Uncle John Shipwreck at 26.2km
Uncle John Shipwreck at 26.2km Vesta Shipwreck at 29km
Vesta Shipwreck at 29km  Raita Shipwreck at 33km
Raita Shipwreck at 33km  Skagit Shipwreck at 34.2km
Skagit Shipwreck at 34.2km Santa Rita Shipwreck at 37km
Santa Rita Shipwreck at 37km Dare Shipwreck at 39km
Dare Shipwreck at 39km Lizzie Marshall Shipwreck at 47km
Lizzie Marshall Shipwreck at 47km Puritan Shipwreck at 48.5km
Puritan Shipwreck at 48.5km Wempe Brothers Shipwreck at 49.4km
Wempe Brothers Shipwreck at 49.4km Duchess of Argyle Shipwreck at 58km
Duchess of Argyle Shipwreck at 58km John Marshall Shipwreck at 62.3km
John Marshall Shipwreck at 62.3km William Tell Shipwreck at 64.2km
William Tell Shipwreck at 64.2km Revere Shipwreck at 69km
Revere Shipwreck at 69km Cyrus Shipwreck at 75km
Cyrus Shipwreck at 75km
Considerably more loss of life and media attention spurred the Canadian government forward and the West Coast Trail and the nearby Pachena Point Lighthouse were born. The Janet Cowan was named after the maiden name of the wife of the first owner. Unlike most other shipwrecks in the Graveyard of the Pacific, a good record of the ship as well as at least a couple photographs of her still exist. The Janet Cowan sailed from Cape Town on September 11th, 1895, bound for Royal Roads(near Victoria) on Vancouver Island. With 1100 tons of ballast and a crew of 29. The long voyage went very well until the evening of December 30th, 1895. Approaching Juan de Fuca Strait, under easy sail and with moderate weather, attempts were made to signal for a tug or pilot. They received no response. With daylight gone, she was sailing blind into the Graveyard of the Pacific. The captain decided to wait for daylight before sailing further. Just after 7pm the wind shifted suddenly and steadily increased into a gale. The Janet Cowan was brought around and attempted to run out for an offing to wait out the storm. At 845pm, Cape Flattery Lighthouse was spotted four or five miles away. The weather continued to worsen, with a violent gale blowing, heavy seas and thick snow falling, the Captain worried that their repeated wearing(a sailing technique of turning through the wind to shift the wind from one side of the boat to the other), would cause them to lose ground. This agonizing battle went on in brutal darkness as they charted their position based on their last sight of Cape Flattery Lighthouse and estimated speed. They pinpointed their position to be about seven miles off Vancouver Island, with the time now being well after midnight. Just before 1am, the second mate reported land on the starboard bow. The crew rushed to steer away, however the ship was caught in the trough of the sea and still inching towards the shore. At 130am the Janet Cowan was perilously inside the outside breakers and unable to escape. The ship was swung broadside on, with her head to the westward and the seas breaking over her fore and aft, she crashed into the shore.
The captain ordered all hands aft and one of the crew, Thomas Chamberlain volunteered to swim ashore with a rope. The attempt failed when the rope became hopelessly tangled in the rocks. He had to let it go to save himself, clawing his way to the shore.
They succeeded on their next attempt, though with tremendous difficulty, by using a lifeboat to get to the shore with a rope. Bitterly cold weather, tumultuous, swirling seas, and overall precarious situation made the lifeboat unusable in getting the crew to the shore. Instead they used the line suspended between the shore and the ship to clumsily bring people over one at a time. In the frantic chaos of that night three of the crew drowned, never to be seen again. It is assumed they drowned while attempting the crossing, however, they were only noticed missing after a muster of the crew by the captain on shore. One final crewman, too afraid to leave the crumbling ship, remained. He eventually made it to shore after daybreak.
Cold, wet and desperate, it was decided to make an attempt to reach Cape Beale Lighthouse and obtain assistance. With this object in view, the crew divided, and the telegraph line being found, it was decided to follow it, the younger members of the crew pushing ahead, and others following as best they could. The captain, who appears to have been worn out from incessant watching before reaching shore, being unable to keep up, the chief officer telling the steward and donkeyman to stay by and assist captain, pushed on himself in the hope of obtaining help. After spending a night in the woods, and finding it impossible to make progress through the heavy snow and dense forests, had no alternative but to return to wreck. On the way back he passed the body of captain. who had died from exposure, also bodies of W. Selkirk, donkeyman, and Peberval, A.B., and other members of the crew; reported death of George Kinnear, cook, from same cause.

The wreck being reached, and sea having moderated, crew were enabled to get on board ship, and proceeded to land provisions and sails for making tents, and then made camp on beach, meanwhile, doing all they could to attract attention of passing vessels. Almost two weeks passed and on the 11th day of January, the steam-tug "Tyee" arrived on the scene and rescued mate and 12 of crew who were in the immediate vicinity of wreck. Leaving nine men in camp higher up on beach, who at the time could not be reached, and after an unsuccessful attempt at reaching them, owing to bad surf and darkness, the tug proceeded to Port Townsend. The nine men were rescued by Canadian steamer Princess Louise on Monday following, and safely landed at Victoria, B.C.

The official court documents of the shipwreck write the following as the cause of the disaster, "The ship appears to have been navigated with proper and seamanlike care, and every precaution taken for the safety of the ship and crew, but in marking the ship's position off on the chart at midnight of the 30th day of December, sufficient allowance does not appear to have been made for current, which, however, seems to have been stronger than usual, and to have set the ship rapidly on the Vancouver shore, the light draught of the vessel, combined with the violence of the gale, with the heavy sea, making it impossible to keep her off."
Shipwrecks Near the Janet Cowan (KM19)
The Varsity Shipwreck Near KM17.6
![]() There are several more shipwrecks relatively near the Janet Cowan on in the Graveyard of the Pacific. The Varsity was a small fishing boat of 90 tons, returning to Puget Sound from California on February 5th, 1940. In bad weather and stormy seas, she abruptly struck the shore, just a kilometre past, what is today, Tsocowis Creek on the West Coast Trail. The Varsity had overrun her position due to the fast northerly current. The crew were so hopelessly lost that they believed their position to still be in American waters, instead of way up on the coast of Vancouver Island. Unfortunately their distress call gave their position as several kilometres south of their actual position. Of the crew of seven, three survived by crawling their way to the shelf below what is now called Valencia Bluffs. They now found themselves on a steep shelf that they could not climb. Out of the wreckage they managed to survive exposure and construct a ladder up the cliff and found the trail that hikers now call the West Coast Trail. The three survivors made their way to Tsocowis Creek and found the Tsocowis cabin occupied by lineman who fortunately was there. The three were later picked up from Tsocowis Beach. Today the shipwreck's huge metal winch rusts in a crevice at the foot of Valencia Bluffs.
There are several more shipwrecks relatively near the Janet Cowan on in the Graveyard of the Pacific. The Varsity was a small fishing boat of 90 tons, returning to Puget Sound from California on February 5th, 1940. In bad weather and stormy seas, she abruptly struck the shore, just a kilometre past, what is today, Tsocowis Creek on the West Coast Trail. The Varsity had overrun her position due to the fast northerly current. The crew were so hopelessly lost that they believed their position to still be in American waters, instead of way up on the coast of Vancouver Island. Unfortunately their distress call gave their position as several kilometres south of their actual position. Of the crew of seven, three survived by crawling their way to the shelf below what is now called Valencia Bluffs. They now found themselves on a steep shelf that they could not climb. Out of the wreckage they managed to survive exposure and construct a ladder up the cliff and found the trail that hikers now call the West Coast Trail. The three survivors made their way to Tsocowis Creek and found the Tsocowis cabin occupied by lineman who fortunately was there. The three were later picked up from Tsocowis Beach. Today the shipwreck's huge metal winch rusts in a crevice at the foot of Valencia Bluffs.
Varsity shipwreck continued here...
The Valencia Shipwreck Near KM18
![]() The Valencia is usually regarded as the worst shipwreck disaster in the Graveyard of the Pacific and the final impetus for the creation of the West Coast Trail. The SS Valencia was an iron-hulled, 1600 ton passenger steamer built in 1882. Originally built for service between Venezuela and New York City, she later became a coastal passenger liner on the west coast of the United States. In 1906 she was wrecked off Cape Beale, near Clo-oose, on the west coast of Vancouver Island. The captain did not take into account the strong northerly current that caused ships to overrun Juan de Fuca Strait by a considerable distance. Blinded by the weather and battered with strong winds and currents, the captain turned the Valencia toward the coast for its run into the strait. Just before midnight on the 22nd of January, she collided with the reef near Pachena Point on the southwest coast of Vancouver Island. The high number of fatalities are estimated to have been between about 140. Varying sources and speculation has resulted in a fair bit of uncertainty on those figures. According to the government report at the time, the official deaths numbered 136. Only 38 men survived the shipwreck and all the woman and children perished. The Canadian government rapidly began work on what would result in the West Coast Trail. A lighthouse was was constructed and regularly spaced shelters along the newly constructed trail. The Valencia shipwreck disaster happened in 1906, the Pachena Point Lighthouse was finished in 1908, and in 1911 the West Coast Trail was completed.
The Valencia is usually regarded as the worst shipwreck disaster in the Graveyard of the Pacific and the final impetus for the creation of the West Coast Trail. The SS Valencia was an iron-hulled, 1600 ton passenger steamer built in 1882. Originally built for service between Venezuela and New York City, she later became a coastal passenger liner on the west coast of the United States. In 1906 she was wrecked off Cape Beale, near Clo-oose, on the west coast of Vancouver Island. The captain did not take into account the strong northerly current that caused ships to overrun Juan de Fuca Strait by a considerable distance. Blinded by the weather and battered with strong winds and currents, the captain turned the Valencia toward the coast for its run into the strait. Just before midnight on the 22nd of January, she collided with the reef near Pachena Point on the southwest coast of Vancouver Island. The high number of fatalities are estimated to have been between about 140. Varying sources and speculation has resulted in a fair bit of uncertainty on those figures. According to the government report at the time, the official deaths numbered 136. Only 38 men survived the shipwreck and all the woman and children perished. The Canadian government rapidly began work on what would result in the West Coast Trail. A lighthouse was was constructed and regularly spaced shelters along the newly constructed trail. The Valencia shipwreck disaster happened in 1906, the Pachena Point Lighthouse was finished in 1908, and in 1911 the West Coast Trail was completed.
Valencia shipwreck continued here...
The Robert Lewers Shipwreck Near KM20
![]() The Robert Lewers was a 185 foot, four masted schooner of 732 tons, built in Port Blakely, Washington in 1889. She was wrecked just past kilometre 19 on the West Coast Trail, just half a kilometre from the Janet Cowen shipwreck, and less than two kilometres from the Valencia shipwreck. The Robert Lewers entered the Graveyard of the Pacific on the 11th of April, 1923. The ship was heading for Bellingham, Washington in ballast from Honolulu with a crew of 14. The circumstances of how Robert Lewers became wrecked on this shore is a depressing tale of unfortunate mishaps. As she entered Juan de Fuca Strait she found little wind and was forced to wait for a tug boat. A tug boat finally arrived to tow her into port. While passing the hawser line from the tug, it became tangled in the masts and rigging, tearing away the Robert Lewers jib boom and head gear. Another attempt was made with hopeful success, until the tow rope snapped. In the confusion, the tug hit a rock and was forced to limp back to Seattle for repairs. Through this ordeal the ship creeped perilously close to shore so the port anchor was released. Moments later the stern of the ship was dragging along the bottom. As the situation became desperate a call was sent out for another tug. An hour and a half passed, waiting for rescue as the ship continued to grind on the reef. When the second tug arrived, it could not get in close enough to attach a line. The wind was picking up so the captain decided to pull the anchor and try to sail out. The wind was far too weak to pull the massive ship away from the rocks and she fell broadside on the beach. The crew abandoned ship and the Robert Lewers remained, battered by waves and in the next few hours, she broke in two and became a permanent part of the Graveyard of the Pacific just offshore of what would later become the West Coast Trail.
The Robert Lewers was a 185 foot, four masted schooner of 732 tons, built in Port Blakely, Washington in 1889. She was wrecked just past kilometre 19 on the West Coast Trail, just half a kilometre from the Janet Cowen shipwreck, and less than two kilometres from the Valencia shipwreck. The Robert Lewers entered the Graveyard of the Pacific on the 11th of April, 1923. The ship was heading for Bellingham, Washington in ballast from Honolulu with a crew of 14. The circumstances of how Robert Lewers became wrecked on this shore is a depressing tale of unfortunate mishaps. As she entered Juan de Fuca Strait she found little wind and was forced to wait for a tug boat. A tug boat finally arrived to tow her into port. While passing the hawser line from the tug, it became tangled in the masts and rigging, tearing away the Robert Lewers jib boom and head gear. Another attempt was made with hopeful success, until the tow rope snapped. In the confusion, the tug hit a rock and was forced to limp back to Seattle for repairs. Through this ordeal the ship creeped perilously close to shore so the port anchor was released. Moments later the stern of the ship was dragging along the bottom. As the situation became desperate a call was sent out for another tug. An hour and a half passed, waiting for rescue as the ship continued to grind on the reef. When the second tug arrived, it could not get in close enough to attach a line. The wind was picking up so the captain decided to pull the anchor and try to sail out. The wind was far too weak to pull the massive ship away from the rocks and she fell broadside on the beach. The crew abandoned ship and the Robert Lewers remained, battered by waves and in the next few hours, she broke in two and became a permanent part of the Graveyard of the Pacific just offshore of what would later become the West Coast Trail.
Robert Lewers shipwreck continued here...
The Woodside Shipwreck Near KM20
![]() Just past the 20 kilometre mark of the West Coast Trail you will find an anchor of the Woodside on the beach. The Woodside, an 87 foot long steamer built in Sooke, BC in 1878. The Woodside provided regular service between Victoria, Port Renfrew, Barkley Sound and Alberni Inlet. On March 12th, 1888, the Woodside lost her rudder and drifted into the rock shelf in front of Trestle Creek. Just past the 20 kilometre mark on the West Coast Trail, the anchor of the Woodside still sits in the middle of the beach. The ship was a total loss, disintegrating over the years with little left but the hauntingly vivid reminder of the wreck, laying rusting on the beach. The improbably located anchor on the beach is a stunning representation of how cool the West Coast Trail is. Emerge from the deep forest and difficult trail, to a desolate feeling, rocky coastline with a huge anchor left here from a shipwreck that happened over a century ago. Extraordinary!
Just past the 20 kilometre mark of the West Coast Trail you will find an anchor of the Woodside on the beach. The Woodside, an 87 foot long steamer built in Sooke, BC in 1878. The Woodside provided regular service between Victoria, Port Renfrew, Barkley Sound and Alberni Inlet. On March 12th, 1888, the Woodside lost her rudder and drifted into the rock shelf in front of Trestle Creek. Just past the 20 kilometre mark on the West Coast Trail, the anchor of the Woodside still sits in the middle of the beach. The ship was a total loss, disintegrating over the years with little left but the hauntingly vivid reminder of the wreck, laying rusting on the beach. The improbably located anchor on the beach is a stunning representation of how cool the West Coast Trail is. Emerge from the deep forest and difficult trail, to a desolate feeling, rocky coastline with a huge anchor left here from a shipwreck that happened over a century ago. Extraordinary!
Woodside shipwreck continued here...
West Coast Trail A to Z




The Valencia Disaster



West Coast Trail Guide




Explore BC Hiking Destinations!

The West Coast Trail

Victoria Hiking Trails

Clayoquot Hiking Trails

Whistler Hiking Trails

Squamish Hiking Trails

Vancouver Hiking Trails


